FluxyContainer
To create a container object, go to GameObject->3D Object->FLuXY->Container. To add a container component to an existing object, go to Component->Physics->FluXY->Container.
Containers simply contain fluid. Each container exposes physical properties of the fluid in them, such as viscosity or turbulence. Containers are always rectangular in shape, you can't have circular or star-shaped containers, but you can specify their width and height. You can also specify what happens when fluid gets close to the container's edges, and what the initial contents of the container are.
Let's go over the container's inspector properties:
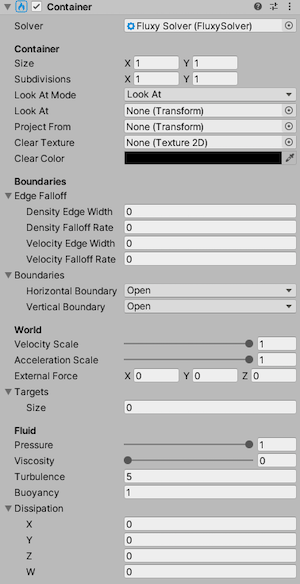
Solver
Reference to the solver in charge of managing this fluid container.
Size
Width and height of this container's domain (in meters).
Subdivisions
Amount of horizontal and vertical subdivisions in the container's domain mesh. Useful for vertex displacement effects.
Look At Mode
Whether the container should just look towards the Look At transform, or copy its orientation.
Look At
If not null, the container will orient itself to look at this transform. Typically, a camera transform would be used here.
Project From
Transform used as the origin point to project targets onto this container. If null, targets will be projected along the container's normal vector. Typically, a camera transform would be used here.
Clear Texture
Texture used to clear the contents of this container.
Clear Color
Color used to clear the contents of this container. Will tint the Clear Texture, if any.
Edge Falloff
Density and velocity falloff at the edges of the container. You can specify both the width of the falloff region (expressed in normalized coordinates), and the falloff rate. This can be used to fade out fluid as it approaches the limits of the container, hiding the fact that simulation only takes place within the container's area.


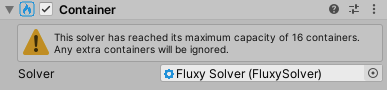
Boundaries
Boundary conditions at the container's edges. This determines what happens when fluid reaches the edge of the container. You can specify the condition for the horizontal and vertical edges independently, and there's 3 different conditions to choose from:
- Open
- Fluid is allowed to flow past the edges of the container.
- Solid
- Edges act as solid walls, fluid is not allowed to flow past them.
- Periodic
- Fluid is allowed to flow past the edge of the container, wrapping to the opposite edge.



Velocity Scale
Percentage of the container's world-space velocity that gets applied to the fluid.
Set both velocity scale and acceleration scale to 0 if you want the fluid to ignore any world-space movement of the container. If you then constrain the container to an object (using Unity's PositionConstraint component, for instance), the results will mimic an infinite simulation domain: fluid will look as if simulated in world-space, the container being just a "window" into the fluid. You can see an example of this in the included InfinitePool sample scene.
Acceleration Scale
Percentage of the container's world-space acceleration that gets applied to the fluid.
External Force
World-space external force applied to the fluid. You can use this to simulate wind, for instance.


Targets
List of target components that should interact with this container. Note the targets listed here will always be considered, in addition to the ones provided by any target provider component (such as FluxyTargetDetector).
Pressure
Percentage of internal pressure applied to the fluid simulation. A value of 1 will strive to remove any divergence from the fluid's velocity field, yielding incompressible fluid. A value of 0 will allow the fluid to freely expand and compress.


Viscosity
Viscosity of the fluid. Viscous fluids will flow slower and come to a rest faster.


Turbulence
Fluid "swirlyness". This determines the amount of curls and vortices in the fluid.


Buoyancy
Density of the fluid relative to the surrounding air. More buoyant fluids will rise up, less buoyant fluids will fall down.


Dissipation
Speed at which fluid density vanishes. You can specify dissipation independently for each of the 4 density channels.